- Before you dismiss the idea that shipping containers can be used for housing, consider this student-housing complex in Amsterdam, as described by The Guardian. Can you imagine something like this on the northwest corner of Burlington’s Main Street/S. Winooski intersection, which has been suggested as a possible site for privately developed UVM student housing?
- The City Council in Portland, Ore., where a “housing emergency” has been declared and where rents have risen more than 20 percent over five years, boosted the city’s affordable housing fund by $64 million. The money comes from a property-tax set-aside, and the council is looking for more revenue sources.
 And one of the councilors has lofted an idea that some other cities beset by under-used mega-athletic complexes might want to seize upon: sell the Portland Coliseum for to a developer who will put affordable housing in its place.
And one of the councilors has lofted an idea that some other cities beset by under-used mega-athletic complexes might want to seize upon: sell the Portland Coliseum for to a developer who will put affordable housing in its place.
- As we’ve noted before, the nationwide initiative to affirmatively further fair housing calls for affordable housing development (at least a good share of it) in low-poverty, “high-opportunity” areas. A country club would seem to fit that description, at least generically. So we were interested to learn that the Planning Board in Mahwah, N.J., recently approved the redevelopment of a country club there for affordable housing.
Before you get too excited, though, you should know about the downside: Much of the land is contaminated from years of pesticide spraying, and the cost of remediation (which includes removal of hundreds of trees) contributed to a reduction in development’s affordable capacity: down from 350 multi-family units to less than 100 single family homes.
- Uber will deliver $1 million to Oakland’s affordable housing fund for the privilege of turning a former Sears building into an office space.
 The deal was prompted partly by fears that Uber’s corporate arrival, with an anticipated 3,000 employees, would lead to gentrification and even higher housing prices.
The deal was prompted partly by fears that Uber’s corporate arrival, with an anticipated 3,000 employees, would lead to gentrification and even higher housing prices.
- Attention, City Market, Hunger Mountain, et al: A food co-op in affordability-challenged Asheville, N.C., is contemplating adding affordable housing to its expansion plans, which also (and less intriguingly) include enlarging its existing store, parking lot and office space.

- Speaking of parking, the Berkeley City Council has voted to target underused parking-lot space for affordable housing development.
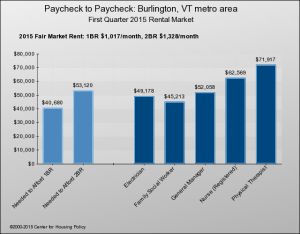
 Council members were reminded at the meeting that the average cost of a 1 bed-room apartment is $1,400 a month, and that’s under rent control! The average cost of an apartment not under rent control? $3,256 a month.
Council members were reminded at the meeting that the average cost of a 1 bed-room apartment is $1,400 a month, and that’s under rent control! The average cost of an apartment not under rent control? $3,256 a month.