Here’s another way to look at the housing-affordability problem: as a damper on economic growth. 
Two economists published a study this summer that essentially made that point. They analyzed growth rates of 220 metropolitan areas and how those rates contributed to national growth from 1964 to 2009. They found, surprisingly, that some of the most productive cities, where pay rates also happen to be high, actually contributed less to overall growth than one might have expected. That’s because employment didn’t grow proportionately in those cities — they cite New York, San Francisco and San Jose in particular — in large part because of housing constraints.
“The main effect of the fast productivity growth in New York, San Francisco, and San Jose was an increase in local housing prices and local wages, not in employment,” write Chang-Tai Hsieh, of the University of Chicago, and Enrico Moretti, of U.C.-Berkeley. “In the presence of strong labor demand, tight housing supply constraints effectively limited employment growth in these cities.”
In other words, workers were prevented from migrating to these productive, high-wage areas because they couldn’t find affordable places to live. By contrast, three-fourths of U.S. growth in those years was attributable to Southern cities and a group of 19 other cities, where housing was more plentiful and wages were lower.

Their article has an overweaning title, “Why do cities matter? Local growth and aggregate growth,” but it’s worth noting their conclusion that the housing constraints in the productive, high-wage cities derived from restrictive or exclusionary land-use regulations. They write:
“Constraints to housing supply reflect both land availability and deliberate land use regulations. We estimate that holding constant land availability, but lowering regulatory constraints in New York, San Francisco, and San Jose cities to the level of the median city would expand their work force and increase U.S. GDP by 9.5%. Our results thus suggest that local land use regulations that restrict housing supply in dynamic labor markets have important externalities on the rest of the country. Incumbent homeowners in high wage cities have a private incentive to restrict housing supply. By doing so, these voters de facto limit the number of US workers who have access to the most productive of American cities.”
And here’s what they say about Silicon Valley, the region between San Jose and San Francisco, which has “some of the most productive labor in the globe. But … by global urban standards, the area is remarkably low density due to land use restrictions. In a region with some of the most expensive real estate in the world, surface parking lots, 1-story buildings and underutilized pieces of land are still remarkably common due to land use restrictions. While the region’s natural amenities—its hills, beaches and parks—are part of the attractiveness of the area, there is enough underutilized land within its urban core that housing units could be greatly expanded without any reduction in natural amenities. Our findings indicate that in general equilibrium, this would raise income and welfare of all US workers.”
Sounds like the technological mecca is plagued by exclusionary zoning.
The economists propose two remedies, neither of which is plausible in the current political climate. One is for the federal government to place limits on locally set land-use regulations. The other is to finance mass transit (such as high-speed trains) that would enable workers to commute to these productive areas without having to live there.
Now then, might any of this translate to Vermont? Consider:
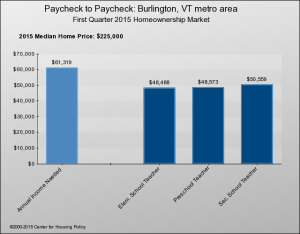
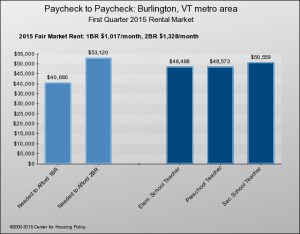
Burlington is an analogue to San Francisco. Of the state’s 19 labor market areas, Burlington/South Burlington’s average annual pay is the highest, by far — $48,529, or about $10,000 more than half the other areas in the state.) Burlington also has an affordable housing shortage that could be termed above average: 61 percent of Burlington’s renters are house burdened (paying more than 30 percent of their income on housing), compared to a state average of 52 percent; and 36 percent are severely house burdened (they pay more than 50 percent), compared to a state average of 26 percent.
So, following their argument, might it be that Vermont would be growing at a higher rate if more workers could afford to live in or near Burlington, one of the state’s highly productive cities? Is Burlington channeling much of its productivity growth into higher housing prices and higher wages?
Perhaps, perhaps not. In Burlington’s favor is a higher rate of employment growth than (3 percent, from 2014 to 2015) than most anywhere else in the state.
On the other hand, employment here might well grow even faster if more workers from the provinces could afford to live here.



 “Builders can’t construct housing because they lack works and workers won’t relocate to the area because they can’t find housing,” The Traverse-City Record-Eagle laments.
“Builders can’t construct housing because they lack works and workers won’t relocate to the area because they can’t find housing,” The Traverse-City Record-Eagle laments.