Chapter 1: The Crunch:
– What do we mean when we say “Vermont has a housing crisis?”
Chapter 2: Emergency housing:
–Resources for people who are homeless (including unsafely housed ) or at risk of becoming homeless
Chapter 3: What is affordable housing:
-What options are there for people who need help paying for their housing, but are not currently homeless?
Chapter 4- Avenues for Advocacy
– What can you do about the affordable housing shortage?

Affordable rental housing (public housing), housing subsidies, mobile homes and homeownership programs.
When we talk about affordable housing, there is often confusion by what we mean. As we covered in Chapter 2 of Housing Demystified, people unfamiliar to the housing advocacy landscape may have some confusion about the difference between emergency housing options – such as shelters – and subsidized housing options, which offer more permanent, subsidized housing solutions. The important thing to remember as you read along is that affordable housing, like emergency housing, can look and be a lot of different things.
What is “affordable housing”?
ffordable housing is generally defined as housing where the resident is paying 30% or less of their household income on housing costs, but even this “rule” is not hard and fast. Most often when we talk about affordable housing, we are referring to subsidized rental housing. But affordable housing may also be “naturally occurring,” or developed privately without federal or state assistance. We will be focusing on intentionally developed affordable housing for this chapter.Some people use “subsidies,” or financial help, to assist in paying their rent. Subsidies can be attached to a particular building, so the “rental unit” or apartment is “subsidized” (project-based vouchers). Housing subsidies may be given to a tenant so that the tenant may use it for a rental of their choice (as is the case with a Housing Choice Voucher). Below we will cover both subsidized rental housing and tenant-based subsidies.
Types of Affordable Housing
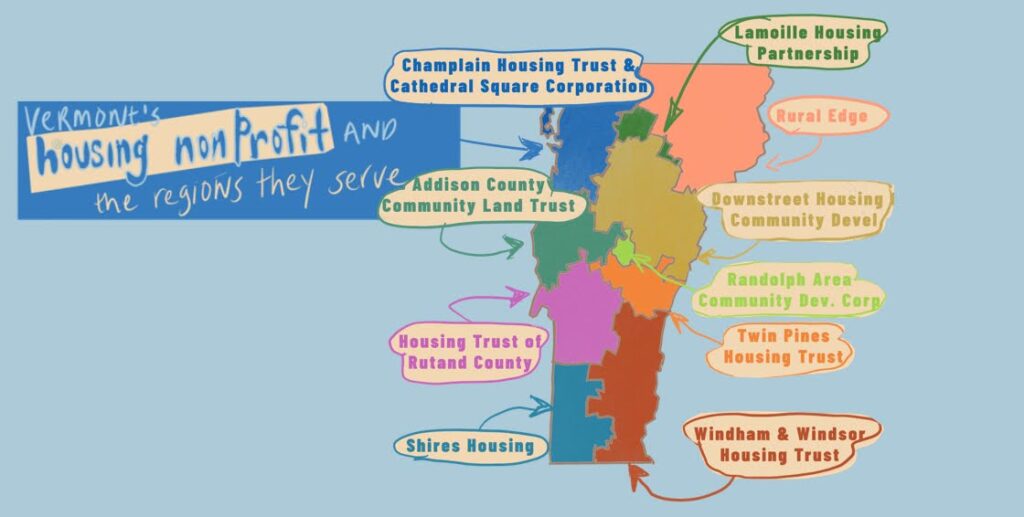
Nonprofit Housing Providers: These are nonprofit organizations across Vermont that receive a variety of funding sources – private and public – which allows them to partner with housing developers to create housing*. Many of these programs provide both rental housing and homeownership programs. Almost all affordable housing providers have a significant waitlist, so would not be a place to go if you are currently in a housing crisis. While the map below includes some of the larger housing nonprofits and the regions they serve, you can access a searchable list of all the affordable housing options in Vermont at HousingData.org
*Some affordable housing providers also develop housing. Affordable housing development is complex, almost always is built with multiple funding streams, and are often partnerships between two or more developers and/or funders
- Eligibility to live in affordable rental housing is determined by income, and affordable housing providers may have different requirements for eligibility.
- Even within the the category of non-profit affordable rental housing, there are different kinds of housing providers
- Vermont hosts a few housing trusts, such as Champlain Housing Trust and Windham and Windsor Housing Trust (among others). Housing trust funds are established sources of funding for affordable housing construction created by governments in the United States. Housing developed by housing trusts are permanently affordable.
- Some affordable housing providers have specialized programs. Of course, there are affordable senior housing providers like Cathedral Square, housing programs for veterans, housing for people in recovery, and for folks with mobility impairments.
- Even within senior housing, there are options:
- Independent Living means that while a person may need to live in a community catered to their specialized needs -such as with other people who are 55 and older, or with other people who have assistive devices to move through the world (like wheelchairs, ventilators, or hearing aids), or with other people who have unique mental or emotional needs- they can meet their basic needs on their own. Independent Living facilities mean just that- each renter can choose when they have their meals, how they schedule their day, when they leave and return to their home. They are also responsible for their basic needs, such as keeping their apartment tidy, removing their garbage, preparing their own meals if they aren’t attending group meals, and arranging their own transportation to appointments.
- Assisted Living describes housing where the resident needs more intensive care, oversight and support. Assisted living facilities can provide nursing care, housekeeping, and prepared meals as needed. Assisted Living housing is more structured than Independent Living, and may have a more rigidity in how a tenant schedules their day.
- Memory Care facilities are a form of residential long-term care that provides intensive, specialized care for people with memory issues. Communities typically feature secure environments where staff can closely monitor the health of the residents.
Housing subsidies – such as the Housing Choice Voucher (otherwise known as Section 8 Voucher), and more recently the Cares Voucher Program- provide financial support for rental housing that the tenant can choose themselves, providing the rent falls within individual program guidelines and meets housing quality standards. Tenants with housing subsidies can rent from private or non-profit landlords. Most often, one would apply for housing subsidies through their local housing authority or Vermont State Housing Authority.
- Vermont Legal Aid has an in-depth, “plain language” description of how housing subsidies work here.
- It is important to note that in Vermont, our state Fair Housing Protected Classes includes receipt of public assistance. This means that in Vermont, it is illegal to discriminate against folks because they are using a housing subsidy, including Housing Choice Vouchers (or Section 8), to afford their living expenses.
Public Housing Authorities (or PHA) are a form of affordable rental housing, sometimes referred to as “public housing” because they are financed by public funding. Vermont has 8 regional Housing Authorities in Barre, Bennington, Brattleboro, Burlington, Montpelier, Rutland, Springfield, and Winooski, and one state housing authority. Housing Authorities provide affordable rental housing and Housing Choice (or Section 8) vouchers. Housing Authorities also provide project-based housing vouchers, or vouchers that are tied to specific properties.
How to Get Affordable Housing
Remember, if you or someone you know is at risk of losing housing now, contact your local Community Action Agency (Chapter 2 of Housing Demystified covers Community Action Agencies) or call 2-1-1 after hours or on the weekends
- Do you already have a housing agency or a site in mind you would like to work with? Reach out directly to that housing agency to ask about their availability and the length of their waitlist. Almost all housing agencies have waitlists, so it’s best to apply to several options if your housing needs may become urgent in the near future.
- To find affordable rental housing, go to HousingData.org – select the region you are looking for, and on the side column you can select any needs you have for your housing.
- Once you have a few options selected, check to see if you meet the eligibility guidelines. You can check to see if you meet their Income Limits by using this HUD Income Limit Checker. For properties with waitlists, call and ask to get on the waitlist, and ask how long they think it may be (they cannot know for sure). You should also ask if they know of availability at other properties.
- Many affordable housing sites accept this Common Rental Application. If you are applying to more than one property, it may be helpful to have a few copies filled out in advance.
If you are facing barriers to finding housing, such as a past eviction, no landlord reference, or overcoming a criminal record, CVOEO’s Vermont Tenants’ Finding Housing Class goes over how to navigate these conversations and how to conduct an organized housing search.
Many people face barriers applying for affordable housing
The Finding Housing class may help navigate barriers to finding housing, but you don’t actually walk away from the class with housing options. Housing is limited and hard to find.
You may also notice it’s challenging to find affordable housing in Vermont if you aren’t able to do the following:
- Speak English
- Access to the internet, a computer, or a printer
- Have a phone
- Have a mailing address
- Understand and navigate complex eligibility requirements and be an expert at their own income sources (for some people, that can be from a variety of subsidies which may or may not count toward income, including SSI, 3Squares, unemployment, ReachUp, and more)
- Have the bandwidth to keep track of multiple housing opportunities
- Understand rights under Fair Housing and Landlord-Tenant Law, and the confidence to enforce them
Still, having access to all those things does not ensure one’s access to housing. We are in a tight housing market. That means that the people who already face high barriers to housing access and who have historically been denied equal access to housing opportunities have an even harder time getting the housing they need.
Need help finding housing?
So what do you do if you need help looking for housing? It depends on what barriers, or challenges, make it hard to apply for housing. If you have a caseworker, you can ask them what assistance they can offer in your housing search. You can also call 211 to ask what your best option might be. (211 can direct you to other resources as well, such as food, fuel assistance, transportation and more!)
- Translation Services: Many housing providers offer translation and HUD requires that programs receiving federal funds provide “meaningful access” to Limited English Proficient (LEP) persons. In other words, if you or someone you know needs assistance understanding English to find and apply for housing, housing providers receiving federal funds should be able to offer extra support. And it doesn’t hurt to ask!
- Disability: Vermont Center for Independent Living (VCIL) can help Vermonters with disabilities access housing, including offering housing support. Remember, disability can be broadly defined an mean a lot of different things. If the ways you think, communicate, process information or move substantially limits your “major life activities,” you should consider accessing resources through VCIL. Major life activities can include accessing housing, job opportunities, and getting meals.
- Aging: We all age! And as we age, our abilities and needs change. Deciding when you need housing support and what that could look like can be hard. Our seniors came of age with different technologies than the ones we rely on today. Fortunately, Age Well Vermont has a hotline for seniors that you can call to talk about your options. You can call 800 642 5119.
- Flight from domestic violence: Domestic Violence (DV) Organizations across Vermont support people fleeing domestic violence through their emergency hotlines, emergency housing programs, and assist program participants find stability through assisting with housing applications, cell phone access, clothing donation services, transportation access, legal services and more.
- We talked about Domestic Violence organizations as part of our coverage of Emergency Housing in Chapter 2.
- The Vermont Network lists DV organizations by county.
- In Vermont, the Fair Housing Act (briefly overviewed in Housing Demystified Chapter 1) includes protections for survivors of abuse, sexual assault, or stalking
- The Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) also offers additional support and protections to survivors of domestic violence. The Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) is a federal law that, in part, provides housing protections for people applying for or living in units subsidized by the federal government and who have experienced domestic violence, dating violence, sexual assault, or stalking, to help keep them safe and reduce their likelihood of experiencing homelessness. Under VAWA, someone who has experienced domestic violence, dating violence, sexual assault, and/or stalking:
- Cannot be denied admission to or assistance under a HUD-subsidized or assisted unit or program because of the VAWA violence/abuse committed against them.
- Cannot be evicted from a HUD-subsidized unit nor have their assistance terminated because of the VAWA violence/abuse committed against them.
- Cannot be denied admission, evicted, or have their assistance terminated for reasons related to the VAWA violence/abuse, such as having an eviction record, criminal history, or bad credit history.
- Must have the option to stay in their HUD-subsidized housing, even if there has been criminal activity directly related to the VAWA violence/abuse.
- Can request an emergency transfer from the housing provider for safety reasons related to the VAWA violence/abuse committed against them.
- Must be allowed to move with continued assistance, if the survivor has a Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher.
- For more information on VAWA Housing Rights and to access the Self-certification form (Form HUD-5382), visit here.
- Remember, anyone can experience domestic violence. DV is a pattern of violence or intimidating behaviors that someone uses to have power and control over an intimate partner. Domestic violence includes physical violence, but also can be emotional, financial or sexual abuse. If you or someone you know is facing unstable housing because of unsafe behaviors of their partner, reach out to one of these organizations.
- To that end, most emergency housing programs provide assistance and case management to help people shift into stable housing. Of course, as we covered in Chapter 2, to access those resources, most often you must meet HUD’s definition of homeless or at risk of homelessness. That means there is a large population of people who either cannot access those resources without falling into a more precarious situation than they are already in, or they cannot access those resources because of the stigma associated with the term “homeless.”
Affordable Homeownership
Vermont has various not-for-profit groups that help guide prospective homebuyers through the homeownership process. These groups provide classes and educational support on topics like home purchase budgeting, foreclosure prevention and mobile home repair.
NeighborWorks Alliance of Vermont
For the most part, these groups are a part of the NeighborWorks Alliance of Vermont. NeighborWorks is a national organization that provides resources, trainings, and networking to Vermont’s five regional homeownership organizations. You will notice that some of the same affordable rental housing providers also provide home ownership assistance, but not all do. Some offer special programs to support people traditionally excluded from housing opportunities, such as Champlain Housing Trust’s Home Ownership Equity Program for Black, Indigenous and People of Color (BIPOC), and Vermont Housing and Finance Agency (VHFA)’s First Generation Homebuyer Program.
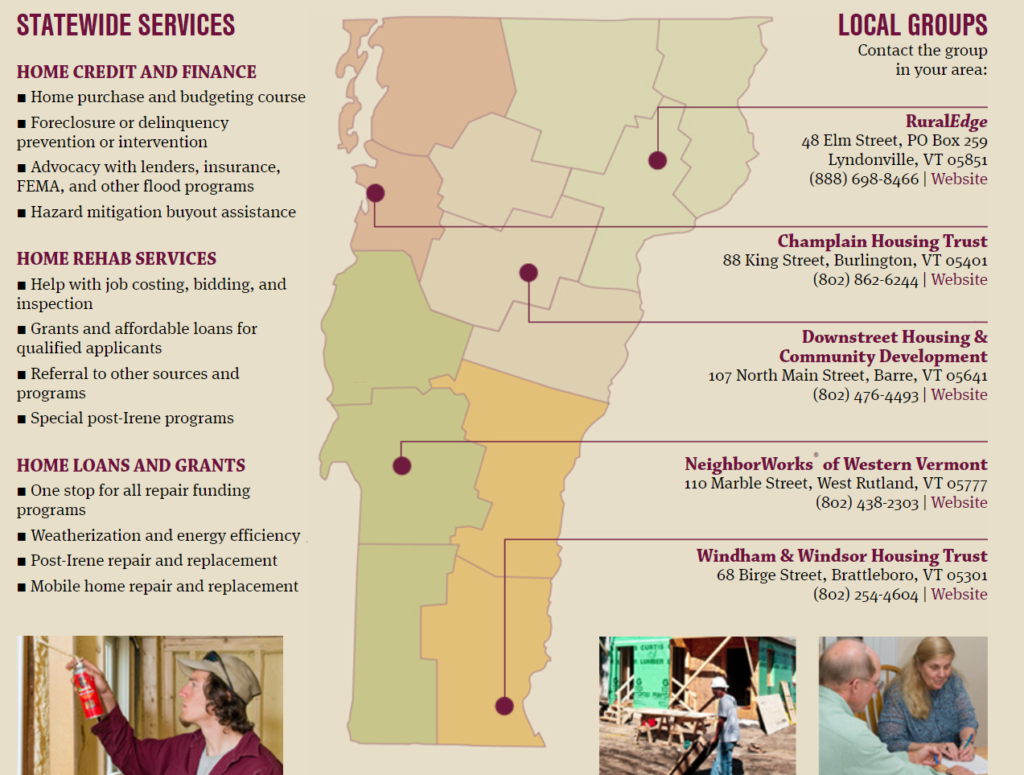
Statewide Homeownership Programs
There are several organizations serving the full state of Vermont which offer home buying support.
- Vermont Housing and Finance Agency (VHFA): Vermont Housing and Finance Agency, or VHFA, provides homebuyer programs, including down payment and closing cost assistance. VHFA works with individuals and banks to help people within a certain income bracket purchase their home with fixed interests rates and sometimes down payment assistance. They have several unique mortgage loan programs targeting specific potential home buyers. Prospective home buyers access these programs through one of the banks that VHFA partners with.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture Rural Housing (USDA): The U.S. Department of Agriculture Rural Housing program of Vermont also provides homebuyer programs, but specifically in rural communities. Rural communities can have unique needs that make affordable housing challenging. For instance, mobile home communities often grant residents the comfort of home ownership, but residents most often are renting the land their home is on, which can make their needs often overlooked when it comes to state housing policies. Rural communities often lack the infrastructure to support housing development, such as sewer systems, and may have limited access to Wi-Fi and cellular service. These barriers are things to consider when we participate in housing advocacy. Tune in for Chapter 4
- Green Mountain Habitat for Humanity serves Lamoille, Chittenden, Franklin and Grand Isle counties. Habitat for Humanity is an organization people are often most familiar with when we talk about affordable home ownership. That is in part because it is a international organization, and there are fulfilling opportunities to volunteer in the home construction process. But Habitat for Humanity also has a unique housing model in that the people who participate in the Habitat program are asked to participate in building the house. This is referred to as sweat equity. Habitat homebuyers help build their own homes alongside volunteers and pay an affordable mortgage. Despite its name recognition and innovative model, the Green Mountain Habitat for Humanity has a limited scope of work. In 2023, the Green Mountain Habitat for Humanity has 7 projects planned, 5 single family homes and two duplexes.
Affordable Housing Funding
Affordable Housing can have very complex funding structures. The way a housing provider is funded will determine what the housing requirements are for the renter or buyer– that is a part of why affordable housing can have such complicated rules around eligibility. Affordable housing and homeownership programs can be funded by Federal, State, and private funding sources. Nowadays, most affordable housing is developed with a mix of all three.
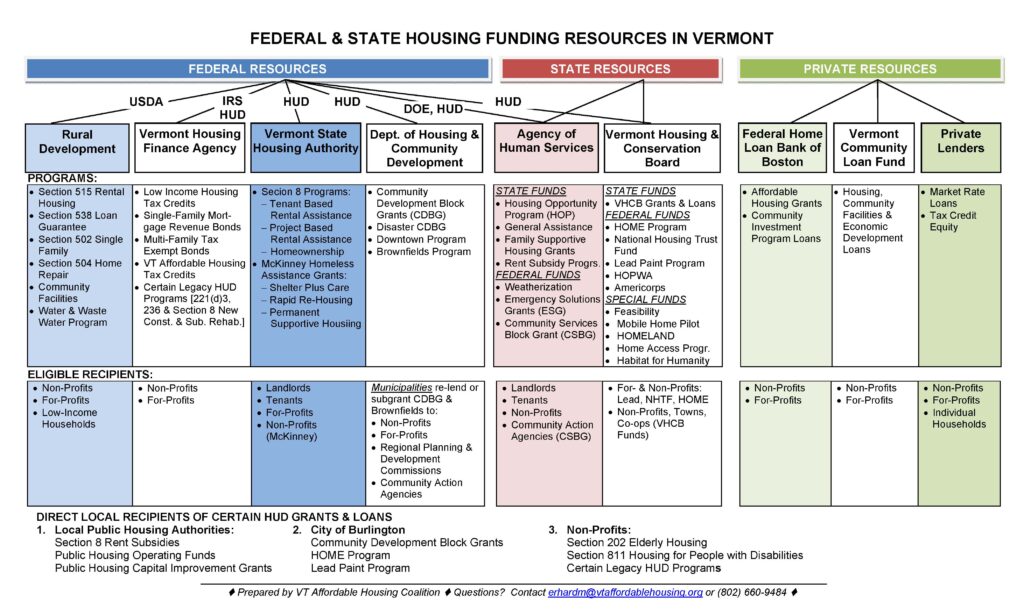
This brings us to the next piece of the affordable housing landscape- affordable housing funders. As you can see from the chart above, our Vermont housing financiers can be designating funding from Federal, State, or private pots of money.
Vermont’s main affordable housing funding nonprofits are Vermont Housing and Conservation Board, Evernorth Housing, and Vermont Housing and Finance Agency.
- Vermont Housing and Conservation Board (VHCB): The Vermont Housing and Conservation board is a unique and powerful resource we have here in Vermont. It was established in the 80’s in a direct response to the ways much-needed housing development was often pitted against land and historical preservation. The Vermont Housing and Conservation Trust Fund Act was enacted in June 1987 with the dual goals of creating affordable housing for Vermonters, and conserving and protecting Vermont’s agricultural land, forestland, historic properties, important natural areas, and recreational lands are of primary importance to the economic vitality and quality of life of the State. VHCB continues to allocate State and Federal funds to nonprofits, towns and co-ops.
- Evernorth Housing: Formerly Housing Vermont, Evernorth Housing now serves communities in New Hampshire and Maine as well as Vermont. Evernorth brings together experienced professional staff to raise capital, invest in and build affordable housing, strengthen the economy, and improve the environment through energy efficiency. They work with community banks and large financial institutions to raise money to finance affordable housing. Here in Vermont, you’ll notice Evernorth often works with our regional affordable housing providers, listed in the section above.
- Vermont Housing and Finance Agency (VHFA): Established by the state legislature in 1974, VHFA promotes affordable housing opportunities for Vermonters. Each state has a Housing Finance Agency. In addition to their home ownership programs, VHFA administers the Federal Low Income Housing Tax Credit Program (a Federal funding source) and the State Affordable Housing Tax Credit Program (revenue raised through the IRS). VHFA also provides financing, development and management support, subsidy administration and tax credits for approximately 8,800 affordable apartments statewide.
In addition, the USDA department of Rural Development, the Vermont State Housing Authority, and the Department of Housing and Community Development are state agencies responsible for allocated federal money.
In some cases, such as Vermont State Housing Authority, Rural Development, and Agency of Human Services, a tenant may receive a subsidy directly from an organization that finances the development of affordable housing. But in most cases, a tenant or potential homebuyer works with either their regional affordable rental housing provider or their regional home ownership center. Now that we have shared an overview of affordable housing, here is the Vermont Housing Resource Chart, last published by the Vermont State Housing Authority in 2019 (click for details). It’s complex!
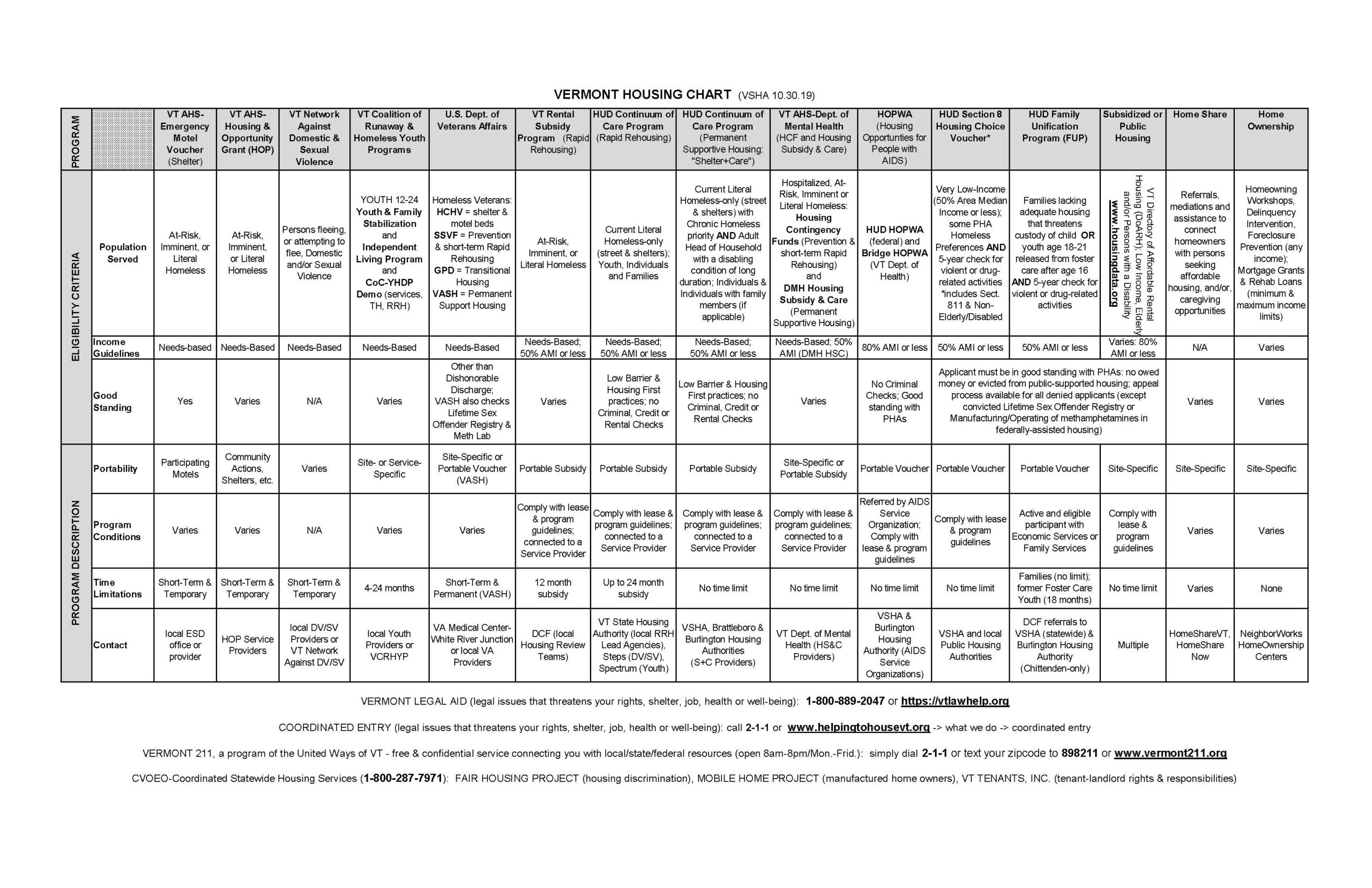
Three points of note: Notice the second column lists population served. This describes the specifications of who the housing is served.
Income guidelines: As we now know, income guidelines can be specific, can change over the years, and are often govern by the sources of funding the housing provider receives.
Portability: Recall that some housing subsidies can be travel with the tenant, and some are site-specific, meaning they stay with a unit of a building. In this column, you can see where these vouchers can be used or if they stay with a unit.
Next Up: Housing Advocacy
Affordable housing is complicated! But having a basic understanding of our affordable housing system is important to do the advocacy we urgently need. Don’t get discouraged if this is a lot to take in- it is for everyone, and many of us become more familiar with our regional infrastructure as we engage with our affordable housing network over time.
Stay tuned for the final chapter of Housing Demystified, Chapter 4, to be published this winter, 2023.
Affordable housing is complicated! But having a basic understanding of our affordable housing system is important to do the advocacy we urgently need. Don’t get discouraged if this is a lot to take in- it is for everyone, and many of us become more familiar with our regional infrastructure as we engage with our affordable housing network over time.




























 The Definitive Guide to Renting in Vermont
The Definitive Guide to Renting in Vermont















